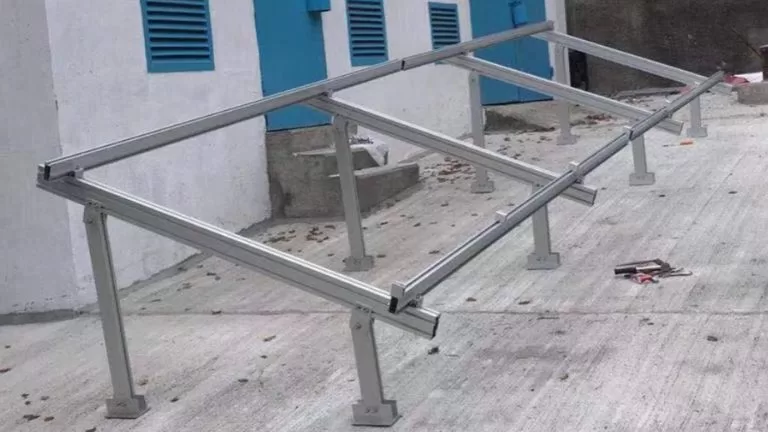
Aluminum Solar Panel Mounting Frames | Structures | Systems
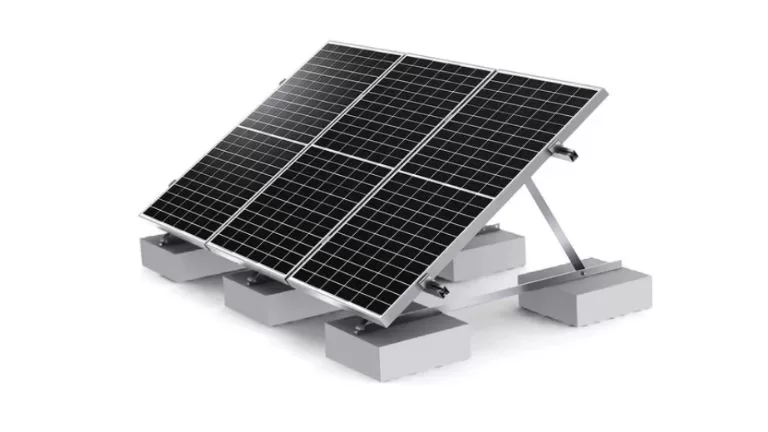

The Aluminum Solar Panel Mounting System is a vital structural component used for securing and installing solar panels, commonly utilized in photovoltaic (PV) projects. Aluminum is the preferred material for these systems due to its lightweight nature, high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and ease of processing. These mounting systems are highly adaptable to various installation scenarios, including rooftop, ground-mounted, and specialized architectural applications such as Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV). Designed for efficiency, safety, and durability, aluminum solar panel mounting systems are a reliable solution for sustainable energy installations.
Fixation and Support Securely attaches solar panels to rooftops, walls, or the ground using rails and clamps.
Optimizing Efficiency Adjustable tilt design helps panels capture more sunlight for better energy production.
Stability-Provides strong support against wind, snow, and other environmental forces.
Panel Protection Includes protective features like rubber pads to prevent damage during installation.
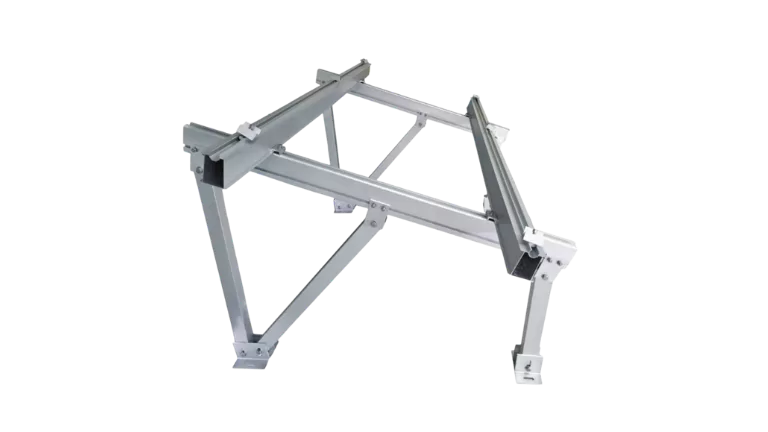

Advantages of Aluminum Mounting Frames
Aluminum alloys are lightweight, strong, and highly resistant to corrosion, making them an excellent choice for solar panel extrusions in mounting systems. These extrusions help reduce the overall system weight, enabling easier transportation and installation, while reliably withstanding various loads in outdoor environments. Aluminum performs exceptionally well in humid and coastal areas due to its natural corrosion resistance. As an eco-friendly material, it is 100% recyclable, supporting sustainability. Additionally, aluminum’s ease of processing allows for the creation of complex structures such as rails, clamps, and brackets to meet diverse installation needs.
| Fonctionnalité | Aluminium | Galvanized Steel | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poids | Lightweight, easy to transport and install | Heavy, adds significant system load | Lighter than galvanized steel but heavier than aluminum |
| La force | High strength, supports various loads | High, suitable for heavy-duty applications | Very high, maintains structural integrity over time |
| Résistance à la corrosion | Excellent, natural oxidation layer prevents rust | Moderate, zinc coating wears off over time | Excellent, resists rust even in harsh environments |
| Environmental Impact | 100% recyclable, eco-friendly | Less eco-friendly due to coating processes | Fully recyclable, more sustainable |
| Ease of Processing | Easy to shape into complex structures | Harder to process, requires specialized equipment | More challenging to process due to hardness |
| Coût | Moderate, affordable for long-term use | Lower initial cost but higher maintenance cost | High initial cost but minimal long-term maintenance |
Main Components of Aluminum Mounting Structures
Aluminum solar mounting structures consist of several key components, including rails, mounting clamps, brackets, rubber pads, bolts and nuts, and base supports. These components work together to provide stability, support, and protection for solar panels during installation and long-term use.
Rails form the backbone of the mounting system, used to align and securely fix solar panels. Aluminum rails are lightweight yet strong, making installation easier. They are connected to walls, rooftops, or supports with bolts or clamps, ensuring a stable framework.
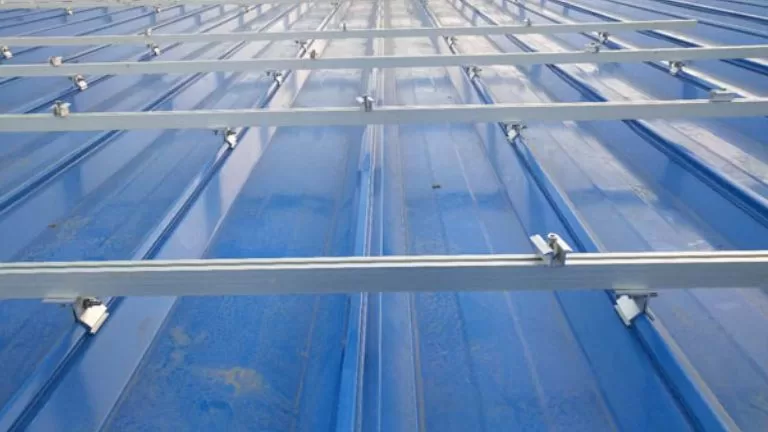

Clamps hold the solar panels in place, preventing movement.
- Pinces intermédiaires: Secure adjacent panels at their connection points to ensure stability.
- Pinces d'extrémité: Lock panels at their edges to keep them tightly fixed. Rubber pads are often added to protect the panels from scratches.
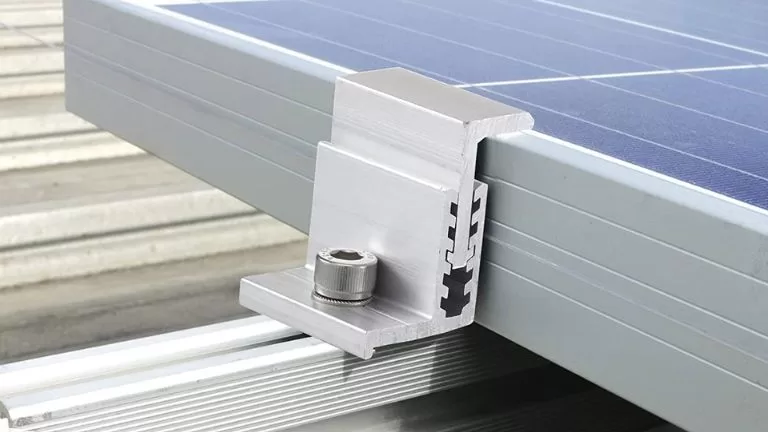

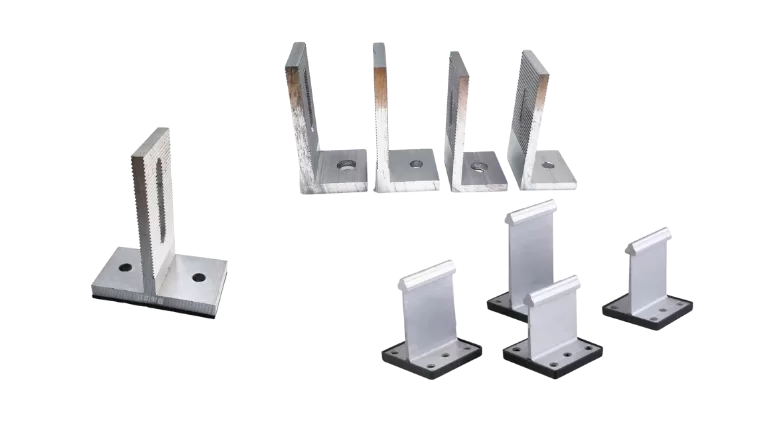
Brackets support the connection between solar panels and the system’s base. They are versatile and designed for different surfaces such as sloped roofs, flat roofs, or ground installations. Adjustable brackets optimize panel angles for better energy efficiency.

Rubber Pad
Rubber pads are placed in clamps or brackets to protect solar panels from scratches and absorb vibrations. They prevent panel movement and reduce wear over time, ensuring system stability and panel longevity.
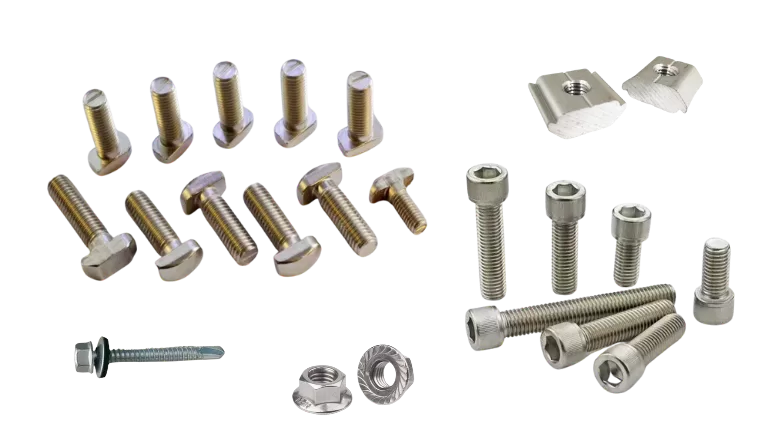
Bolts & Nuts
Bolts and nuts, made from durable aluminum or stainless steel, secure the components together. They resist loosening and corrosion, ensuring a strong and stable structure with minimal maintenance.

Base Supports
Base supports provide a stable foundation for the mounting system. Aluminum bases are lightweight, durable, and designed to withstand wind and snow loads. Adjustable designs ensure compatibility with uneven surfaces or roof types.

Types of Solar Mounting Systems
Solar mounting systems can be grouped into several types, each designed for specific installation scenarios and structural requirements. The four common types are roof-mounted systems, ground-mounted systems, carport systems, and tracking systems.
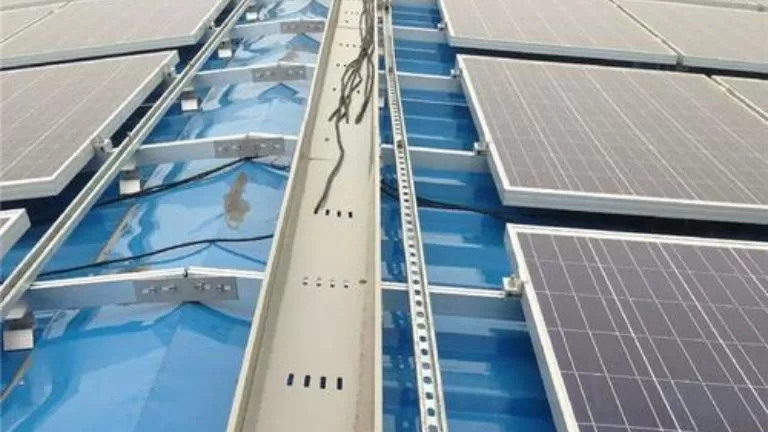
Roof-Mounted Systems
Roof-mounted systems are designed for installing solar panels on residential or commercial building rooftops.
- Sloped Roofs: Panels are mounted on tiled or metal roofs using hooks connected to rails, providing secure attachment without damaging the roof.
- Flat Roofs: These systems often include adjustable tilt frames to optimize sunlight exposure. Non-penetrating designs such as ballasted foundations are commonly used to protect the roof’s structural integrity.

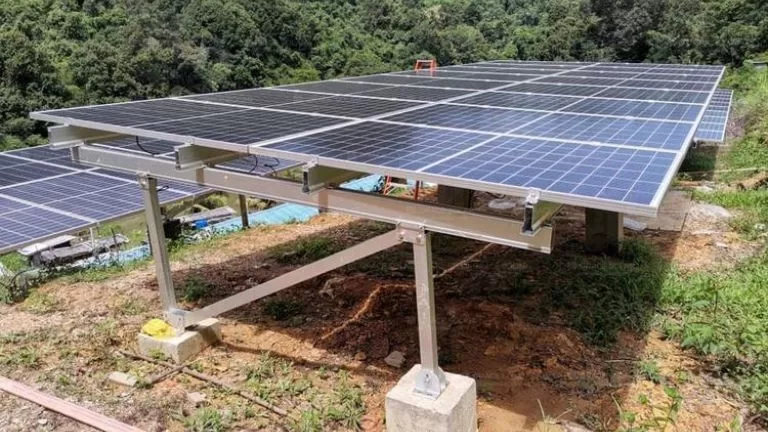
Systèmes au sol
Ground-mounted systems are ideal for large-scale solar farms and projects. Panels are supported by aluminum frameworks and steel piles anchored to the ground. These systems are highly durable, with strong resistance to wind and snow loads. Their flexible design allows adjustment of height and tilt angles to suit the terrain and maximize energy generation.

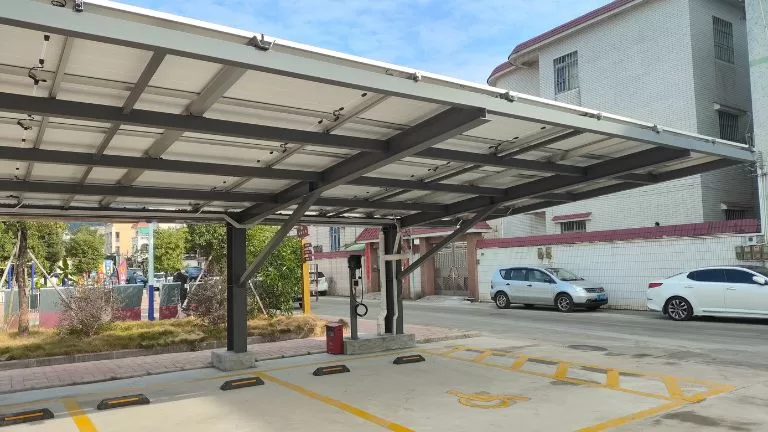
Carport Systems
Carport systems combine solar energy generation with practical vehicle protection. Solar panels are installed as the roof of the carport, providing shade and protection for parked vehicles while producing electricity. These systems are suitable for residential driveways, commercial parking lots, and public spaces. Additionally, carports can be designed to integrate electric vehicle (EV) charging stations, enhancing their functionality and convenience.

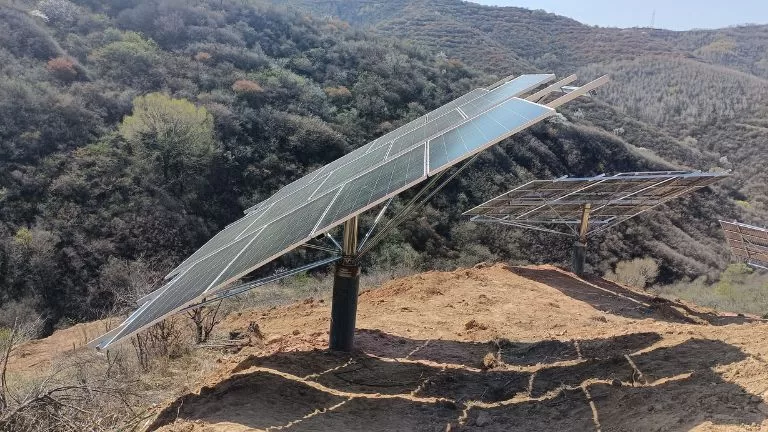
Tracking Systems
Tracking systems follow the movement of the sun to maximize energy output.
- Single-Axis Tracking: Panels rotate around one axis, usually horizontally or vertically, to track the sun’s path.
- Dual-Axis Tracking: These systems rotate along two axes for optimal sunlight capture throughout the day, achieving the highest efficiency among tracking systems.

Mounting Frames Surface Treatment Technologies
The surface treatments for aluminum mounting frame aim to enhance their corrosion resistance and aesthetic appearance, making them more durable and suitable for various environments. The main treatment methods include:
1. Anodizing:
This treatment increases the surface hardness and corrosion resistance of aluminum by forming a protective oxide layer. It provides long-term durability and is available in finishes such as silver or black, which also improve the system’s appearance. Anodizing is particularly effective in preventing rust or wear in outdoor conditions.
2. Powder Coating:
Powder coating adds an additional protective layer to the aluminum surface, improving its resistance to scratching, fading, and corrosion. This technology also allows for customized color designs to meet specific aesthetic or branding needs while maintaining durability in various environments.
3. Electrophoresis Coating :
This technique creates a smooth and uniform surface coating, offering superior protection against corrosion and wear. It is especially well-suited for coastal or high-humidity areas as it enhances resistance to salt spray and other environmental challenges. The resulting finish ensures both longevity and an attractive appearance.
How to Choose Aluminum Solar Mounting Systems
Selecting the right aluminum solar mounting system is crucial for ensuring durability, efficiency, and compatibility with your project. The following key points should be considered during the selection process:
1. Material Quality:
Opt for high-quality aluminum alloys such as 6063 or 6005 to guarantee excellent corrosion resistance and structural strength. These materials ensure long-term reliability and durability in different environments.
2. Installation Requirements:
Identify the type of project—whether it’s roof-mounted, ground-mounted, or building-integrated photovoltaic (BIPV). Choose a system design specifically tailored to the project scenario to maximize efficiency and simplify installation.
3. Environmental Adaptability:
Consider the environmental conditions of the installation site. For areas with high humidity, salt spray, or extremely cold climates, select aluminum materials treated with anodizing or electrophoresis coating to enhance resistance and durability.
4. Load-Bearing Capacity:
Evaluate the wind and snow loads in the local area as well as the weight of the solar panels. Ensure that the mounting system meets or exceeds the load-bearing requirements to maintain safety and performance under harsh conditions.
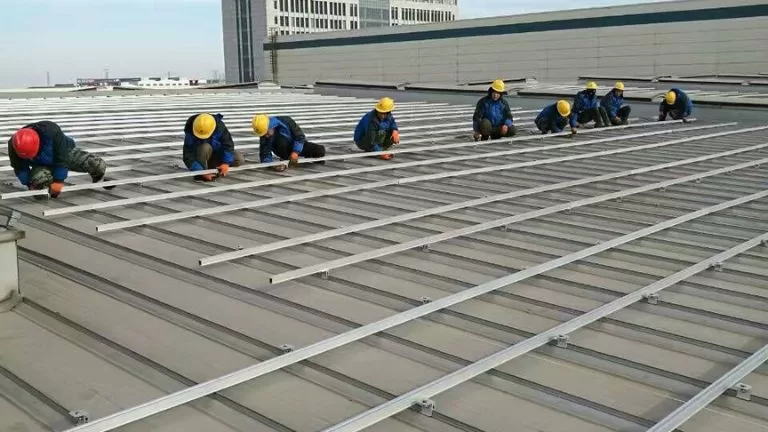

Solar Mounting Structures Installation Process
The installation of aluminum solar mounting structures involves several key steps to ensure a stable and efficient setup. Below is a step-by-step guide:
1. Prepare the Site:
Clear the roof or ground area of debris and check the existing infrastructure to ensure it has sufficient load-bearing capacity for the mounting system and solar panels.
2. Install Rails:
Following the design blueprints, secure the aluminum rails to the brackets or foundations. Use the appropriate bolts and fasteners to ensure the rails are securely attached and properly aligned.
3. Install Clamps:
Use mid clamps to fix adjacent solar panels together and end clamps to secure the panels at the edges. Ensure all clamps are tightly connected to the rails to avoid any panel movement.
4. Adjust the Angle:
Adjust the tilt angle of the solar panels based on local sunlight conditions to maximize energy generation efficiency.
5. Inspection and Reinforcement:
Inspect each fastener and connection point to ensure they are secure. Verify that the entire system is stable and free from loose components, making necessary adjustments to reinforce the structure where needed.
