Aluminum Doors | Windows Frame Processing Equipment
Overview
The production process of aluminum profile doors and windows unfolds with the initial step of precision cutting of aluminum profiles. Subsequently, the profiles undergo meticulous drilling and slotting processes to create the necessary openings and configurations. Finally, the carefully prepared components are skillfully assembled, bringing together the various elements to craft the finished aluminum doors and windows.

1. Aluminum section cutting
Aluminum profile cutting involves the use of cutting equipment to sever aluminum alloy profiles based on the length dimensions specified in the design drawings and cutting sheets for aluminum alloy doors and windows.
The cutting equipment for aluminum alloy profiles is categorized into profile cutting saws and corner bracket cutting saws based on their functional use.
Among the profile cutting saws, there are further distinctions: frame profile cutting saws and glass bead cutting saws based on the material being cut.
Additionally, they can be categorized by the number of saw heads, with options such as single-head cutting saws and double-head cutting saws. Precision in cutting is achieved through various types, including ordinary cutting saws, precision cutting saws, and CNC cutting saws.
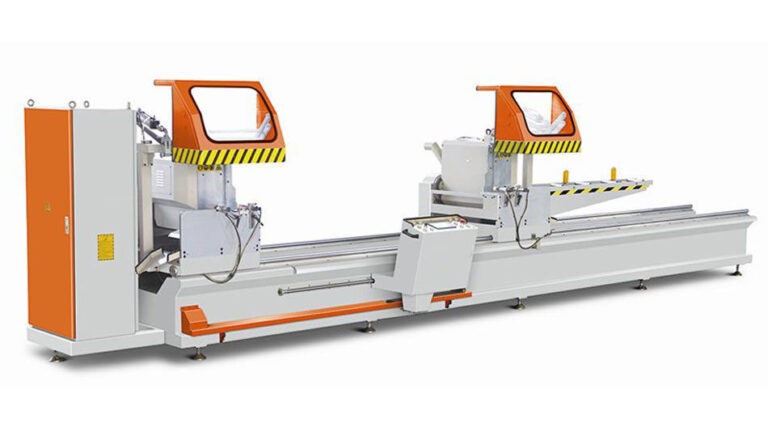

As the level of automation in door and window manufacturing continues to rise, CNC machining tools have become widely adopted and applied in the production processes. One key component in this evolution is the CNC cutting saw, characterized by several notable features:
Automatic Adjustment of Cutting Angles: The cutting angles are automatically adjusted, enhancing the precision and efficiency of the cutting process.
Utilization of High-Precision Imported Saw Blades: The CNC cutting saw employs high-precision imported saw blades, ensuring a smooth finish on the cut surfaces.
Batch Processing of Multiple Profile Dimensions: It allows the simultaneous input of dimensions for several profiles, facilitating continuous cutting of profiles with different lengths.
Direct Input for Sawing Length Dimensions: The sawing length dimensions can be directly inputted, eliminating the need to return to reference points when changing the cutting length.
Sequential Labeling of Cut Profiles: The CNC cutting saw is capable of printing and labeling stickers for the sequential order of cut profiles.
Precision Control of Movable Saw Heads: The movable saw heads are driven by ball screw mechanisms, ensuring high precision in fixed lengths.
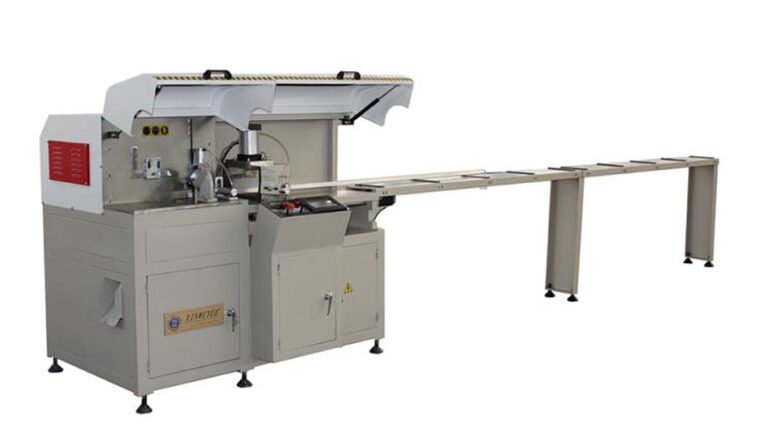

The cutting saw plays a pivotal role in the aluminum alloy door and window cutting process, and the quality of the cut profiles depends on three main factors: radial runout, axial runout, and the quality of the saw blade. Radial and axial runout determine the size and angle discrepancies in the cut profile section, while the quality of the saw blade determines the surface roughness of the cut section, subsequently influencing the quality of door and window assembly.
Hard alloy saw blades encompass various parameters, including tooth shape, angle, number of teeth, blade thickness, blade diameter, and the type of hard alloy used. These parameters collectively determine the processing capacity and cutting performance of the saw blade. Proper selection of saw blade parameters is crucial when aiming for optimal cutting performance based on specific requirements.
2. Component Machining
To complete the assembly of aluminum alloy doors and windows, the profiled bars, once cut, undergo additional machining processes according to the processing techniques, design blueprints, and the installation requirements of hardware components. Mechanical machining equipment or specialized devices are employed to mill, punch, drill, and perform other processes on the profiled bars, ensuring that the assembly requirements of the finished doors and windows are met.
2.1 Milling Drain Grooves
Processing Equipment: Copy Milling Machine
Description: The copy milling machine has a template board preprocessed with various required openings. The milling cutter then mechanically processes the profiled bars following the predetermined hole and groove trajectories. Copy milling machines are classified into single-axis, double-axis, and multi-axis variations, primarily used for processing various shapes of slots, tenons, drainage holes, pressure balance holes, and more in aluminum alloy doors and windows.
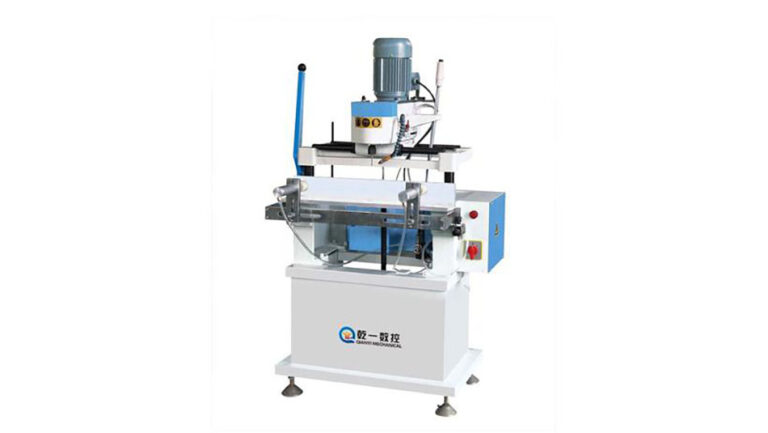

2.2 Milling Assembly Tenons
Processing Equipment: End Milling Machine
Description: The end milling machine is suitable for processing the stepped surfaces, rectangular grooves, tenon heads, and other various shapes on the ends of aluminum profiles. In the assembly of horizontal or vertical frames in aluminum alloy doors and windows, the ends of the horizontal or vertical frame materials are processed according to the matching end surfaces of the outer frame profile, using the end milling machine for milling the assembly end face of the profiled bars.
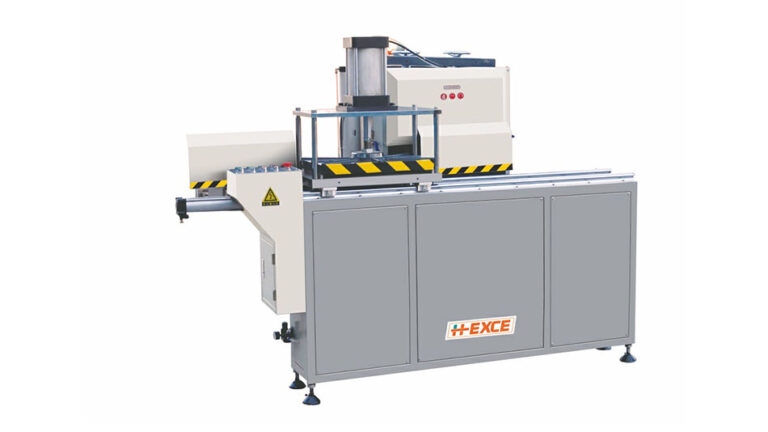

2.3 Milling (or Punching) Fan Materials
Processing Equipment: Copy Milling Machine or Punch Press
Description: The assembly notches, slide track notches, lock notches, grooved convex surfaces with edges, pulley notches, and handle slot (or hinge slot) for push-pull aluminum alloy doors and windows assembly can be machined using copy milling machines or punch presses.
2.4 Drilling (or Punching) Holes
Processing Equipment: Drilling Machine or Punch Press
Description: Various holes required for the assembly of aluminum alloy push-pull doors and windows, such as assembly holes (top, bottom, sides), corner installation holes (or combination holes), stop block installation holes, buffer pad installation holes, assembly holes for the fan, pulley installation holes, and installation holes for fixed and open windows frames, hinges, and handles, are all processed using drilling (or punching) machines.
3. Assembly of aluminum doors | windows frame
The assembly process for aluminum alloy doors and windows involves combining various components, hardware elements, seals, glass, and accessories into a cohesive, fully-finished product.
The assembly of hardware components includes the assembly of the bottom pulley for doors and windows, the assembly of locks, the assembly of hinges and rods, and the assembly of handles.
3.1 Assembly Method
The most common facade form for aluminum alloy doors and windows is rectangular. Therefore, the assembly of aluminum alloy doors and windows frames or sashes typically involves a 45-degree butt joint. There are at least six assembly techniques for 45-degree butt joints: screw connection, riveting, extrusion, pulling, expansion, and welding. Currently, most door and window manufacturing enterprises primarily adopt the extrusion assembly process (also known as collision or riveting), while a small number of enterprises use the adjustable corner bracket screw connection process.
Extrusion Assembly Process: This process involves using a corner assembly machine to press the aluminum profiles’ bottom surface, tightly combining it with the corner bracket. This method works by having the extrusion cutter of the corner assembly machine press into the surface of the aluminum profile. The deformation of the aluminum profile causes the corner bracket to be fixed inside the profile cavity, connecting the two aluminum alloy profiles. Extrusion assembly has advantages such as high efficiency, large-scale production in the factory, high levels of mechanization, and the introduction of CNC four-head corner assembly machines has further automated the production of aluminum alloy doors and windows.
Assembly with Adjustable corner bracket: In this method, holes are pre-drilled on the aluminum profile according to the hole positions on the adjustable corner bracket. The corner bracket is then secured inside the profile using screws, connecting the two aluminum alloy parts. The advantages of this method include:
- The use of high-strength connection bolts for adjustable corner bracket, avoiding distortion of the profile cavity (no distortion of external dimensions) and preventing the problem of the fourth corner offset.
- The ability to readjust the adjustable corner bracket if there is misalignment during assembly.
- The possibility of on-site assembly, allowing aluminum alloy profiles to be cut, holes punched for the adjustable corner bracket, and then directly shipped with hardware and other components for on-site assembly.
- The ability to assemble doors and windows at non-90-degree angles.
- The need for mold processing for adjustable corner bracket, and the limitation of use in large cavities, causing gaps when assembling in small cavity areas.
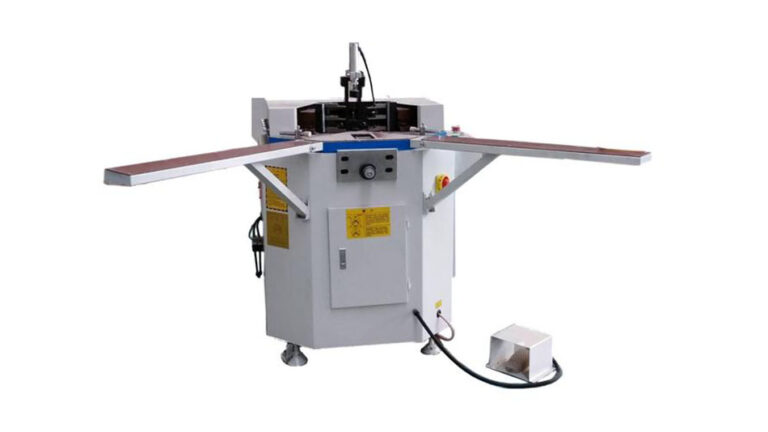
3.2 Corner Assembly Equipment
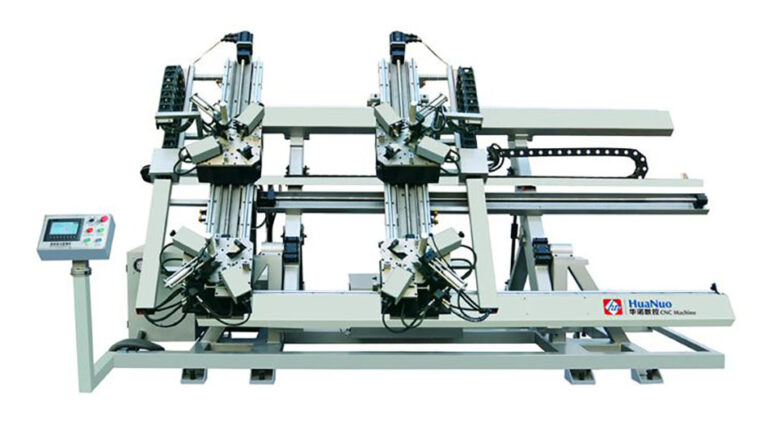
For extrusion assembly, the main types of equipment are single-head corner assembly machines, double-head corner assembly machines, and four-head corner assembly machines. Single-head machines assemble one corner at a time, double-head machines assemble two corners simultaneously, and four-head machines assemble four corners at once, completing the assembly of a door or window frame or sash in one go. Due to the high precision requirements of four-head corner assembly, it generally involves CNC operation for high automation.
Single-Head Corner Assembly Machine Features:
- Hydraulic system control for stable and reliable operation.
- Synchronous feeding of left and right punch heads to avoid deformation during the corner assembly process, ensuring a firmer window corner connection.
- Synchronous feeding mechanism simplifies machine adjustments.
- Threaded adjustment for the distance between upper and lower corner assembly knives, facilitating convenient knife alignment.
- Configurable single-knife multi-point corner assembly knives for more reliable assembly of thermal break aluminum doors and windows.

Four-Head CNC Corner Assembly Machine Features:
- Can complete the corner bracket-style stamping connection of all four corners at once, achieving high production efficiency.
- The clamping device moves automatically forward and backward, making operation convenient, with automatic adjustment of window size.
- Automatic pre-tightening of all four corners is achieved through torque monitoring by the servo system.
- Convenient adjustment of corner assembly knives in both forward and backward directions to meet the needs of different profiles.
- One-time frame assembly allows control of the joint seams and flatness between profiles, ensuring predictable frame quality.
Factory

HTS NEW MATERIALS is a professional aluminum extrusion profile manufacturer based in China. We specialize in various stages of aluminum profile production, from mold design and melting to extrusion, oxidation, electrophoresis, coating, and polishing, providing a comprehensive range of services.
Our product range encompasses aluminum profiles suitable for windows and doors (including thermal break section), industrial applications (T-slot, channel, tubing), and photovoltaic systems. Situated in Jiangxi, our spacious production facility covers 30,000 square meters and employs over 200 skilled professionals, enabling us to produce more than 10,000 metric tons of aluminum profiles annually.
At HTS NEW MATERIALS, we also offer various surface treatments, including anodizing, electrophoretic coating, powder coating, PVDF coating, and wood grain transfer printing, to enhance both functionality and appearance. Whether it’s for construction, industry, or renewable energy, our high-quality aluminum profiles are ready to meet your specific needs.
